Imagine you could use only three parameter sets of a hydrological model to represent the modelling uncertainty in the flood frequency analysis. Imagine how many more input scenarios could be then analysed at a lower computational cost. This study assists you in selecting such three parameter sets that could be assumed as representative for the full parameter ensemble.
Continue reading “A novel method for downsizing the model parameter ensemble”Posts
New session on multi-techniques at EGU21
Call for abstracts for a new session at the EGU General Assembly 2021!
Are you working with multi-dataset, multi-objective or multi-model techniques in hydrologic or water quality modelling?
Then our new HS2.3.7 session on Multi-dataset, multi-variable
and multi-objective techniques to improve prediction of hydrological
and water quality models organized together with David C. Finger & Alberto Montanari is just the right for you!
New objective function to account for discharge data uncertainty
Calibration data for hydrological models are uncertain
Discharge data used to calibrate and evaluate hydrological models can be highly uncertain and this uncertainty affects the conclusions that we can draw from modelling results. In this work, we investigated the role of discharge data uncertainty in hydrological model calibration to give recommendations on methods to account for data uncertainty.
Continue reading “New objective function to account for discharge data uncertainty”WomenInHydrology initiative
Leaky pipeline
Plenty of evidence exists for gender biases in geoscience fields (including hydrology) leading to a disproportional decline of female scientists as they advance in their career. This phenomenon has been already spotted by Alper in 1993 and described as the leaky pipeline.
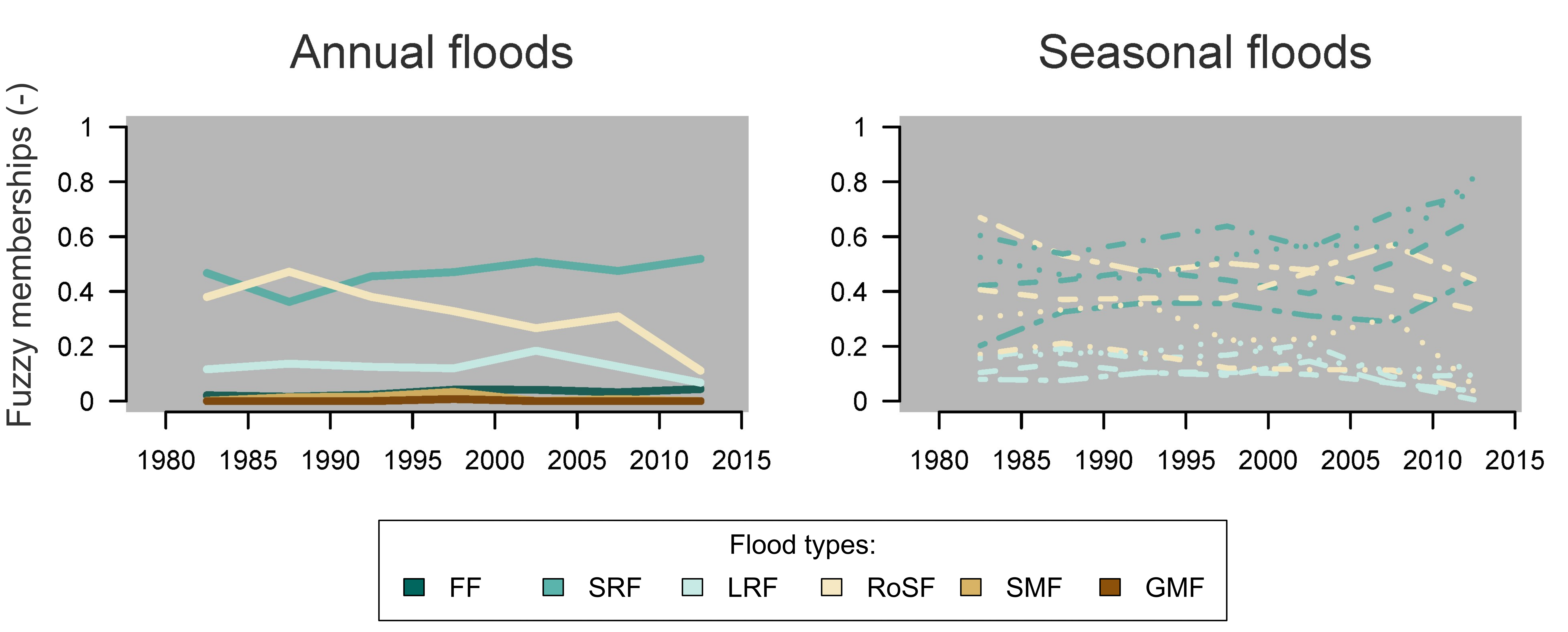
Continue reading “WomenInHydrology initiative”Shifts in the dominant flood-types in alpine catchments as due to climate change
Traditional trend analysis of floods
In many places, magnitudes and frequencies of floods are expected to increase due to climate change. To understand these changes better, trend analyses of historical data are helpful. However, traditional trend analyses do not address issues related to shifts in the relative contributions of rainfall versus snowmelt floods, or in the frequency of a particular flood type.
Continue reading “Shifts in the dominant flood-types in alpine catchments as due to climate change”The latest work is now in open discussion of NHESS
Representative ensemble for simulation of extreme floods
This work proposes methods for reducing the computational requirements of hydrological simulations for the estimation of very rare floods that occur on average less than once in 1000 years. These methods enable the analysis of long time streamflow series (here for example 10 000 years) at low computational costs with representing modelling uncertainty. They are to be used within continuous simulation frameworks with long input time series and are readily transferable to similar simulation tasks.
Continue reading “The latest work is now in open discussion of NHESS”A novel ensemble-based conceptual-data-driven approach
In our latest paper, we propose a novel framework for ensemble-based streamflow simulations. This framework develops a conceptual-data-driven approach (CDDA) that integrates a hydrological model (HM) with a data-driven model (DDM) into a hybrid modelling approach.
Continue reading “A novel ensemble-based conceptual-data-driven approach”