Imagine you could use only three parameter sets of a hydrological model to represent the modelling uncertainty in the flood frequency analysis. Imagine how many more input scenarios could be then analysed at a lower computational cost. This study assists you in selecting such three parameter sets that could be assumed as representative for the full parameter ensemble.
Continue reading “A novel method for downsizing the model parameter ensemble”Tag: extremes
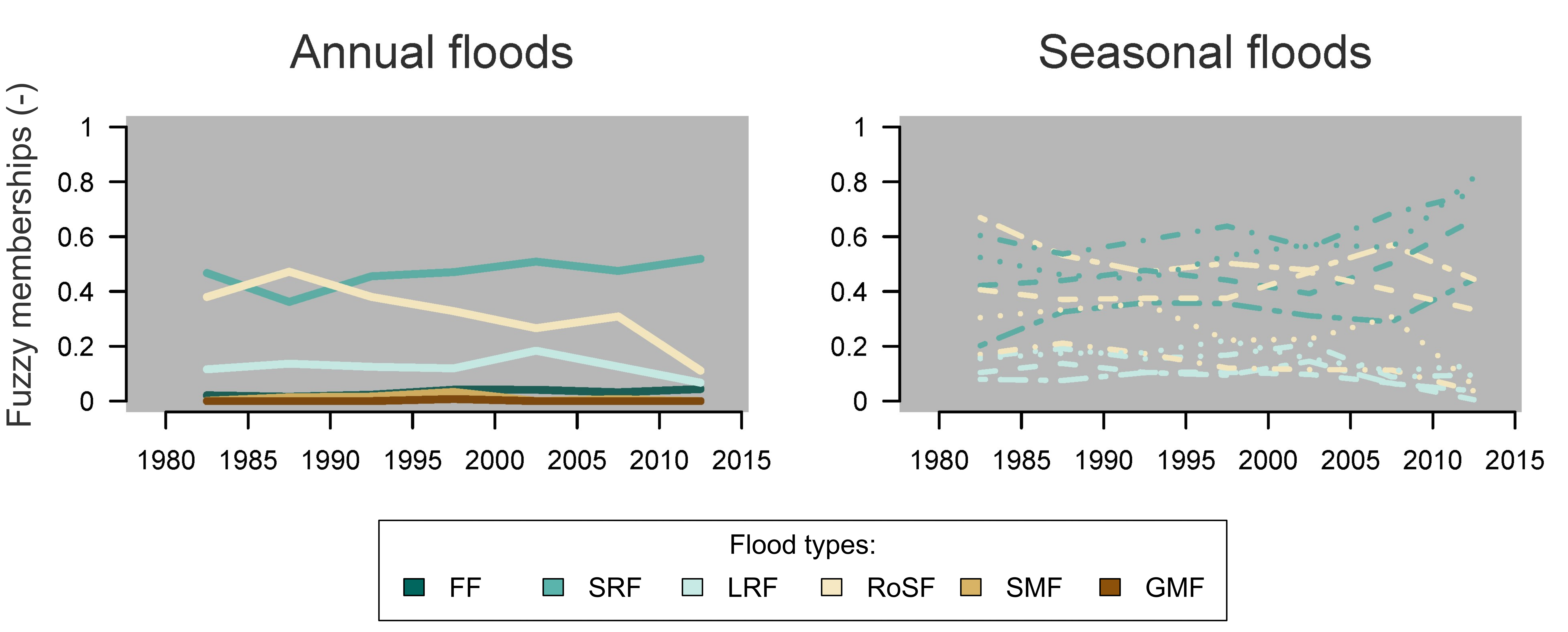
Shifts in the dominant flood-types in alpine catchments as due to climate change
Traditional trend analysis of floods
In many places, magnitudes and frequencies of floods are expected to increase due to climate change. To understand these changes better, trend analyses of historical data are helpful. However, traditional trend analyses do not address issues related to shifts in the relative contributions of rainfall versus snowmelt floods, or in the frequency of a particular flood type.
Continue reading “Shifts in the dominant flood-types in alpine catchments as due to climate change”The latest work is now in open discussion of NHESS
Representative ensemble for simulation of extreme floods
This work proposes methods for reducing the computational requirements of hydrological simulations for the estimation of very rare floods that occur on average less than once in 1000 years. These methods enable the analysis of long time streamflow series (here for example 10 000 years) at low computational costs with representing modelling uncertainty. They are to be used within continuous simulation frameworks with long input time series and are readily transferable to similar simulation tasks.
Continue reading “The latest work is now in open discussion of NHESS”